How to operate a drone? It’s more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting safety regulations, and appreciating the incredible possibilities of aerial perspectives. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and control mastery to capturing stunning aerial footage and navigating legal complexities. Whether you’re a novice eager to take flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, prepare for an informative journey into the world of unmanned aerial vehicles.
We’ll cover everything from basic flight controls and safety protocols to advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and FPV flying. We’ll also explore the legal considerations and best practices to ensure you operate your drone responsibly and legally. By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to confidently handle your drone and capture breathtaking aerial content.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying safe operating conditions, and understanding emergency procedures. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves checking the drone’s battery, propellers, and GPS signal strength. Ensure the battery is fully charged and properly connected. Examine the propellers for any damage or wear. A strong GPS signal is essential for accurate positioning and control.
| Check Item | Procedure | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | Check battery level indicator and physically inspect for damage. | Battery fully charged and no visible damage. | Low battery level, swelling, or physical damage. |
| Propellers | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, bends, or damage. | All propellers intact and undamaged. | Cracks, bends, or other damage to any propeller. |
| GPS Signal | Observe the GPS signal strength indicator on the drone’s controller or app. | Strong, stable GPS signal with minimal satellite loss. | Weak or unstable GPS signal, frequent satellite loss. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check gimbal for smooth movement and proper functionality. | Gimbal moves smoothly and accurately. | Gimbal is stiff, jerky, or unresponsive. |
| Flight Controller | Ensure all lights and indicators on the flight controller are functioning correctly. | All lights and indicators show correct status. | Malfunctioning lights or indicators. |
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is paramount. In case of a malfunction, immediately attempt to return the drone to its home point using the RTH (Return-to-Home) function. If RTH fails, try to regain control manually, prioritizing a safe landing in a clear area. If the drone becomes uncontrollable, cutting power is the last resort.
Safe Operating Distances

Maintaining safe distances from people, obstacles, and restricted airspace is non-negotiable. Keep a minimum distance of at least 30 meters from people and buildings. Avoid flying near power lines, tall structures, or other potential hazards. Always check for and adhere to local airspace restrictions.
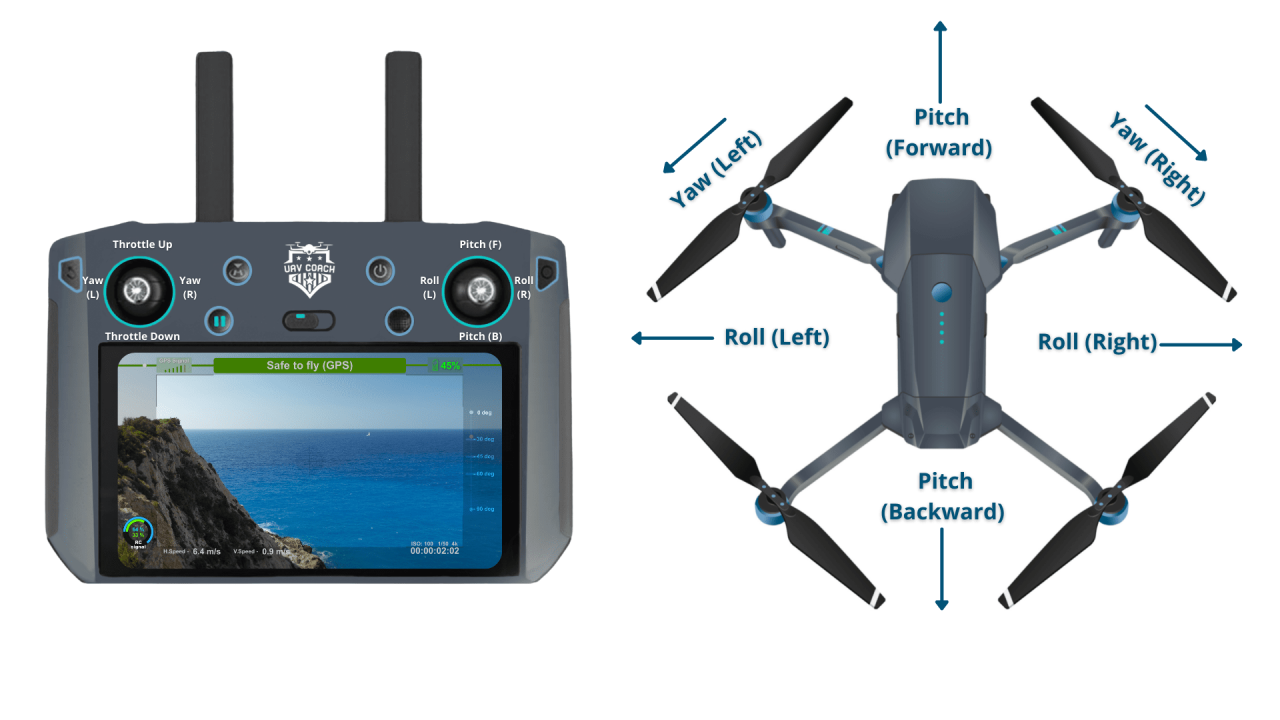
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Effective drone operation requires a solid understanding of its controls and flight modes. Different drones utilize various control methods, and selecting the appropriate flight mode is crucial for safety and performance.
Drone Controls
Most drones use joysticks for primary control, offering precise maneuvering. Many also incorporate mobile apps providing intuitive control and access to additional features like camera settings and flight planning. Some advanced drones offer alternative control schemes, such as voice control or gesture recognition.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability and control for novice pilots. Sport mode allows for faster speeds and more agile maneuvers. Manual mode offers complete control, but demands significant experience and skill.
Calibration and Maneuvers
Calibrating the drone’s compass and sensors is essential for accurate flight. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate these components. Smooth and controlled maneuvers, such as takeoff, landing, and hovering, are achieved through gradual joystick movements and precise control inputs. Practice in a safe, open area.
Navigation and Flight Planning
Precise navigation and flight planning are key to successful drone operations, especially for complex missions. Utilizing GPS coordinates and waypoints allows for pre-planned flight paths, ensuring safe and efficient flights. Understanding wind conditions is also crucial for safe and predictable flight.
GPS Coordinates and Flight Planning
GPS coordinates provide precise location data, enabling the creation of detailed flight plans. Many drone apps allow users to input coordinates to define waypoints and create a flight path. This is particularly useful for aerial photography or surveying tasks.
Sample Flight Plan
- Takeoff from designated launch point.
- Ascend to a pre-determined altitude (e.g., 30 meters).
- Fly in a straight line for 50 meters.
- Hover for 10 seconds to capture footage.
- Turn 90 degrees to the right.
- Fly in a straight line for another 50 meters.
- Initiate return-to-home function.
- Land at the original launch point.
Waypoints and Return-to-Home
Waypoints are pre-programmed locations that the drone will automatically navigate to. The return-to-home (RTH) function automatically guides the drone back to its starting point, a crucial safety feature in case of signal loss or other emergencies.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal requirements, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure you’re fully prepared before your first flight.
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both the operator and the surrounding environment.
Wind Conditions
Wind significantly affects drone flight. Strong winds can make controlling the drone difficult, potentially leading to accidents. Always check the weather forecast before flying and avoid flying in high-wind conditions.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding drone camera settings and composition techniques. Adjusting settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows for optimization of image quality in various lighting conditions. Careful composition enhances the visual appeal of your aerial shots.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
Maintain a steady flight to avoid blurry footage. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique shots. Use the drone’s zoom capabilities to focus on specific details. Understand the effects of lighting on your images and videos, and adjust your settings accordingly.
| Camera Setting | Description | Effect on Image/Video | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. | Higher ISO = brighter image, more noise; Lower ISO = darker image, less noise. | Higher ISO in low light, lower ISO in bright light. |
| Shutter Speed | The length of time the camera’s shutter stays open. | Faster shutter speed = sharper image, less motion blur; Slower shutter speed = more motion blur, potentially creative effects. | Faster shutter speed for moving subjects, slower shutter speed for motion blur effects. |
| Aperture | Controls the amount of light entering the camera. | Wider aperture (lower f-stop) = shallower depth of field, blurred background; Narrower aperture (higher f-stop) = greater depth of field, everything in focus. | Wider aperture for portraits, narrower aperture for landscapes. |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring optimal performance. This includes cleaning, battery care, and proper storage. Knowing how to troubleshoot common problems can save time and prevent costly repairs.
Regular Maintenance
Clean the drone’s body and propellers after each flight to remove dirt and debris. Store the drone in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight. Properly charge and store batteries to maximize their lifespan.
Common Problems and Solutions
- Problem: Drone won’t power on. Solution: Check battery level and connections.
- Problem: Weak GPS signal. Solution: Fly in an open area with clear sky visibility.
- Problem: Propeller malfunction. Solution: Inspect and replace damaged propellers.
- Problem: Camera malfunction. Solution: Check camera settings and connections.
- Problem: Drone is unresponsive. Solution: Recalibrate the drone’s compass and sensors. Try restarting the drone.
Proper Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from extreme temperatures and moisture. Keep batteries charged to around 50% capacity for long-term storage. Avoid storing the drone in direct sunlight or near sources of heat.
Replacing Damaged Parts
Replacing damaged parts usually involves removing the broken part and installing a new one. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or online tutorials for specific procedures. Always use genuine replacement parts to ensure proper functionality and safety.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone legally and responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and laws. This includes identifying restricted airspace, obtaining necessary permits, and being aware of situations where drone operation is prohibited or unsafe.
Regulations and Laws

Regulations vary by region. Familiarize yourself with the specific laws and regulations governing drone operation in your area. These laws typically cover aspects such as registration, licensing, flight restrictions, and operational guidelines.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Many areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. It is crucial to identify and avoid these areas. Apps and online resources often provide information on restricted airspace.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need to obtain permits or licenses before operating a drone. These permits often require background checks and adherence to specific operational guidelines.
Illegal or Unsafe Operation
Flying over crowds, near critical infrastructure, or in inclement weather is generally illegal and unsafe. Unauthorized drone flights near airports or other restricted areas can lead to serious consequences. Always prioritize safety and legal compliance.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced drone techniques involve mastering complex maneuvers and utilizing advanced features. This includes acrobatic movements, obstacle avoidance, autonomous flight modes, and FPV (First-Person View) flying. These techniques require significant practice and skill.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Acrobatic maneuvers like flips, rolls, and other aerial stunts require precision and control. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area away from obstacles and people. Always prioritize safety over attempting complex maneuvers.
Obstacle Avoidance and Autonomous Flight
Many advanced drones feature obstacle avoidance systems, which use sensors to detect and avoid obstacles. Autonomous flight modes allow the drone to fly pre-programmed routes without constant pilot input. These features enhance safety and efficiency.
FPV (First-Person View) Flying
FPV flying uses goggles or a screen to display a live video feed from the drone’s camera, providing an immersive flying experience. This requires advanced piloting skills and careful attention to safety.
Complex Drone Maneuver: A Sample Step-by-Step Guide (Example: Figure-Eight)
- Take off and ascend to a safe altitude.
- Maintain a steady hover.
- Begin a smooth left turn, gradually increasing speed and banking angle.
- Continue the turn, creating the top half of the figure-eight.
- As you complete the top half, initiate a smooth right turn.
- Continue the right turn, creating the bottom half of the figure-eight.
- Complete the figure-eight and return to a hover.
- Slowly descend and land the drone.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical skill, responsible decision-making, and a keen awareness of safety regulations. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental knowledge and practical steps needed for safe and successful drone flights. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot. Embrace the challenge, explore the skies responsibly, and capture stunning visuals that will leave a lasting impression.
Safe flying!
Essential Questionnaire
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight and anytime you suspect interference (e.g., near metal objects).
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store batteries in a cool, dry place at around 50% charge to prolong their lifespan.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If the signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. Always remain aware of your drone’s location.
Can I fly my drone in any location?
No. Check local regulations and airspace restrictions before flying. Many areas, including airports and national parks, have restricted airspace.
